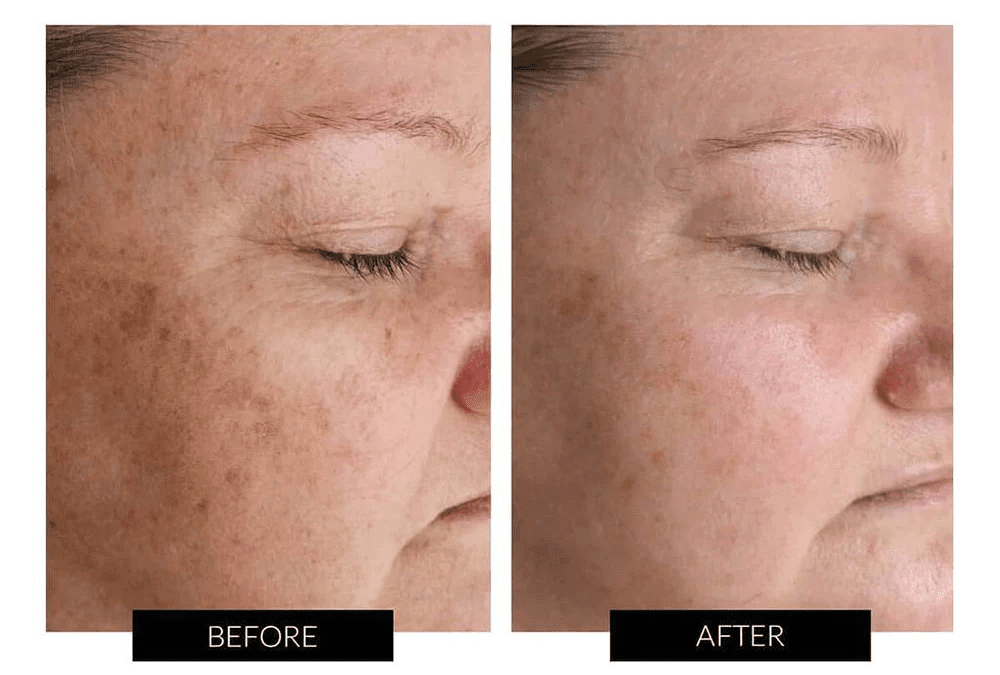
Melasma is a common skin condition that affects many individuals, predominantly women, causing brown patches on the face. Although often mistaken for general pigmentation, melasma has distinct characteristics and triggers. In this blog, we will delve into melasma, its differences from general pigmentation, potential causes, and management strategies.
Firstly, what is Melasma?
Melasma is a skin condition characterised by patches of darker skin on areas of the face, including the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and chin. It can also appear on other sun-exposed areas of the body. These patches usually have a symmetrical pattern and are typically more pronounced in individuals with darker skin tone.
Understanding Pigmentation
Pigmentation refers to the colouring of the skin, which is determined by the presence and activity of melanin, a pigment produced by melanocytes in the skin. Pigmentation can vary from person to person, influenced by genetics, exposure to the sun, hormonal changes, and other environmental factors. These are more of a spot / circular shape.
Differences Between Melasma and General Pigmentation
Causes
- Melasma: Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy or while using hormonal contraception, are primary triggers for melasma. Sun exposure and genetic predisposition also play significant roles. Melasma often improves in the winter and worsens in the summer due to sun exposure.
- General Pigmentation: General pigmentation can be caused by a range of factors, including sun exposure, aging, hormonal changes, inflammation, skin injuries, or skin disorders. It does not have the hormonal association seen in melasma.
Appearance
- Melasma: The patches in melasma are distinct and have a characteristic symmetrical pattern. They often appear as irregularly shaped, well-defined brown patches on the face.
- General Pigmentation: Pigmentation due to other factors can manifest in various forms, including freckles, age spots, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and sunspots. The appearance may vary based on the cause.
Location
- Melasma: Commonly affects areas of the face that are exposed to the sun, especially in women. It rarely occurs on non-facial skin.
- General Pigmentation: Can occur on various parts of the body, including the face, neck, chest, arms, and legs, depending on the cause.
Managing Melasma
Managing melasma requires a multifaceted approach involving lifestyle changes, sun protection, and specific treatments. Here are some common strategies:
Sun Protection
- Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF daily, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, especially if spending extended time outdoors.
- Protective Clothing: Wear hats, sunglasses, and clothing that covers the skin to minimize sun exposure.
Topical Treatments
- Hydroquinone: A common topical agent that lightens dark patches of skin.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Can be used in combination with other agents to help lighten the skin.
- Retinoids: Can help improve skin texture and promote even skin tone.
Chemical Peels and Microdermabrasion
- Chemical peels: Can help in exfoliating the skin and reducing the appearance of melasma.
- Microdermabrasion: A non-invasive procedure that can also aid in reducing pigmentation.
As laser specialists we do not recommend that laser and IPL is used to treat melasma as the heat and energy can cause the pigment itself to become darker or come back worse. We do however recommend LED Phototherapy. Why?
Dermalux LED Phototherapy is a non-invasive light treatment that uses LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology to address various skin concerns, including melasma. It’s a popular treatment known for its effectiveness in stimulating skin rejuvenation, reducing hyperpigmentation, and improving overall skin health.
How Dermalux LED Phototherapy Works…
Dermalux LED Phototherapy uses specific wavelengths of light (typically red, blue, and near-infrared) to target different skin concerns. The light penetrates the skin at different depths, stimulating various cellular processes within the skin.
- Red Light: Red light at specific wavelengths can stimulate collagen production and improve blood circulation. It can help in reducing the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation.
- Blue Light: Blue light is often used to target acne-causing bacteria and can help in managing acne and breakouts.
- Near-Infrared Light: Near-infrared light penetrates deeper into the skin, promoting healing and tissue repair. It can help in reducing inflammation and improving overall skin texture.
Dermalux LED Phototherapy for Melasma
Melasma is a complex condition that primarily involves excess melanin production in the skin. While LED Phototherapy can help with overall skin rejuvenation and will provide improvement in the appearance of melasma we do recommend a combination of treatments and skincare products to help manage the skin concern.
I appreciate there is a lot of information here but I am hoping this will help you to differentiate and understand the difference between pigmentation and melasma and why we ask when we get enquiries what your pigmentation looks like. Once we have established what type of pigmentation, we are dealing with we can then tailor a treatment specifically for you.
We can treat Laser and IPL for Pigmentation and offer skincare products for that too and we can treat chemical peels, Dermalogica facials, Dermalux LED Phototherapy and skincare products for Melasma and Louise at LK Aesthetics can help with Microdermabrasion. LK Aesthetics.
If you have any further questions, please do let us know.
Thank you for reading
Amy x
#togetherwehaveyoucovered